[ReactThreeFiber] Matreial - Texture Maping
Texture Maping
메쉬 표면에 이미지 맵핑을 사용해서 보다 사실적인 재질을 표현하기 위한 기능
MeshBasicMaterial - MeshLambertMaterial - MeshPhongMaterial - MeshStandardMaterial - MeshPhysicalMaterial
순으로 많은 매핑을 제공한다.
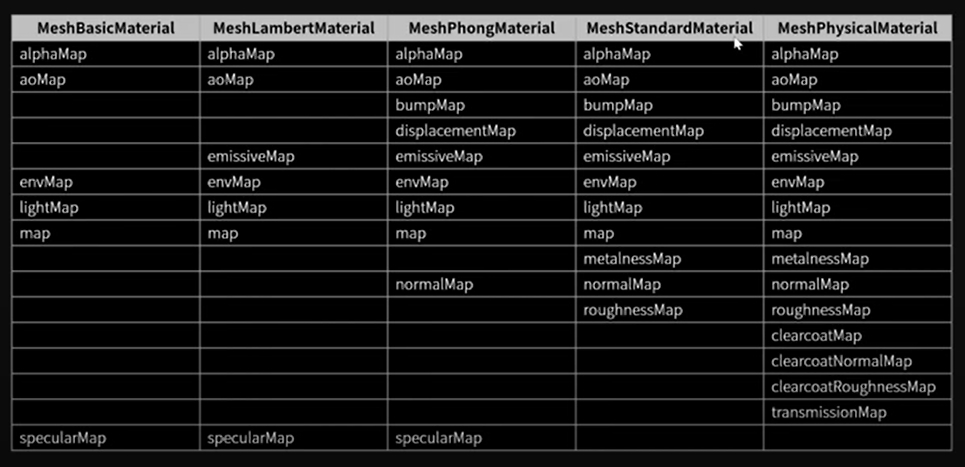
예시
대표적인 메쉬인 MeshStandardMaterial를 사용한다.
https://3dtextures.me/2020/07/15/glass-window-002/의 이미지를 예시로 사용한다.
public/images 안에 다운로드 받은 사진들을 담는다.
const textures = useTexture({
map: '../glass/Glass_Window_002_basecolor.jpg',
roughnessMap: '../glass/Glass_Window_002_roughness.jpg',
metalnessMap: '../glass/Glass_Window_002_metallic.jpg',
normalMap: '../glass/Glass_Window_002_normal.jpg',
displacementMap: '../glass/Glass_Window_002_height.png',
aoMap: '../glass/Glass_Window_002_ambientOcclusion.jpg',
alphaMap: '../glass/Glass_Window_002_opacity.jpg',
});
const mesh = useRef();
useEffect(() => {
textures.map.repeat.x =
textures.displacementMap.repeat.x =
textures.aoMap.repeat.x =
textures.roughnessMap.repeat.x =
textures.metalnessMap.repeat.x =
textures.normalMap.repeat.x =
textures.alphaMap.repeat.x =
4;
textures.map.wrapS =
textures.displacementMap.wrapS =
textures.aoMap.wrapS =
textures.roughnessMap.wrapS =
textures.metalnessMap.wrapS =
textures.normalMap.wrapS =
textures.alphaMap.wrapS =
THREE.MirroredRepeatWrapping;
textures.map.needsUpdate =
textures.displacementMap.needsUpdate =
textures.aoMap.needsUpdate =
textures.roughnessMap.needsUpdate =
textures.metalnessMap.needsUpdate =
textures.normalMap.needsUpdate =
textures.alphaMap.needsUpdate =
true;
mesh.current.geometry.setAttribute('uv2', new THREE.BufferAttribute(mesh.current.geometry.attributes.uv.array, 2));
}, []);
return (
<>
<OrbitControls />
<ambientLight intensity={0.3} />
<directionalLight position={[0, 1, -8]} intensity={0.8} />
<directionalLight position={[1, 2, 8]} intensity={0.8} />
<mesh ref={mesh}>
<cylinderGeometry args={[2, 2, 3, 256, 256, true]} />
<meshStandardMaterial
side={THREE.DoubleSide}
map={textures.map}
roughnessMap={textures.roughnessMap}
roughnessMap-colorSpace={THREE.NoColorSpace}
metalnessMap={textures.metalnessMap}
metalness={0.5}
metalnessMap-colorSpace={THREE.NoColorSpace}
normalMap={textures.normalMap}
normalMap-colorSpace={THREE.NoColorSpace}
normalScale={2}
displacementMap={textures.displacementMap}
displacementMap-colorSpace={THREE.NoColorSpace}
displacementScale={0.2}
displacementBias={-0.2}
aoMap={textures.aoMap}
alphaMap={textures.alphaMap}
transparent
alphaToCoverage
/>
</mesh>
</>
map 속성은 입력받은 텍스쳐 객체를 메쉬 표면에 표현해준다.
side={THREE.DoublesSide} - 메쉬의 양면에 표현하기 위해 사용
roughnessMap
거칠기가 밝은 부분은 약하고 어두운 부분은 심한데 이걸 제대로 보여주기 위해서 roughnessMap-colorSpace{THREE.NoColorSpace} 를 사용한다.
metalnessMap
metalnessMap={textures.metalnessMap}를 바로 적용하면 달라진게 거의 없다. 왜냐하면 현재 meshStandardMaterial의 metalness의 기본값이 0인데 metalnessMap의 값과 곱해지면서 metalness가 적용되는 방법이기 때문이다. 따라서 metalness={0.5}를 입력해준다.
또한, roughness와 같은 논리로 metalnessMap-colorSpace={THREE.NoColorSpace}를 추가한다.
normalMap
노말 벡터(법선 벡터)를 알고있어야 있어야한다.
어떤 면에 대한 수직방향의 벡터
벡터를 이용해서 광원에 대한 음염효과를 변경할 수 있다.
노말 벡터에 대한 값을 지정하기 위해 텍스쳐 이미지를 사용할 수 있다.
평평한 표면에 입체감과 미세한 깨짐을 표현하는 이미지 광원의 쉐이딩 연산에 사용해 시각적으로 입체감을 나타내도록 한다. 실제로 도형에 대한 높낮이는 없는 눈속임에 불과하지만 입체감을 표현하기 위해 좋은 방법이다.
노말 벡터는 xyz값으로 나타내는 방향 벡터인데 이미지 픽셀의 RGB값을 노말 벡터의 xzy값으로 대응하여 나타낸다.
normalScale={2} - 기본값은 1, 더 키우면 음영효과가 더 강해진다. 1 이하도 가능
displacementMap
텍스쳐 이미지를 이용해서 실제 지오메트리의 정점 좌표를 변경해서 입체감을 표현한다.
색상이 밝을 수록 지오메트리의 정점을 더 많이 변경시키며, 변경 방향은 노말 벡터와 동일하다.
하지만 크게 변화하는 것을 느낄 수 없는데 wireframe을 적용해서 확인해보면 지오메트리의 정점이 거의 없는 단순한 구조인 것을 알 수 있다. 구성 좌표를 늘리기 위해서 <cylinderGeomethry args={[2, 2, 3, 256, 256, true]} /> 로 segments를 변경해주고 다시 확인해보면 변화를 확인할 수 있다.
지오메트리의 정점을 변경시키면서 메시의 크기가 커졌다. 이를 원래의 크기로 되돌리기 위해서 displacementcale={0.2},displacementBias={-0.2} 추가
좌표가 많아야하기 때문에 노말맵보다 많은 메모리와 연산값을 필요로한다.
Ambient Occlusion Map
메쉬표면에 미리 만들어 놓은 그림자
완전하게 표현하기 위해서는 두 가지 추가해야한다.
- 광원에 ambientLight 효과 추가 - 없으면 표현안됨
- 지오메트리에 uv2 추가
alphaMap
색상이 어두울수록 투명하고, 밝을수록 불투명하게 표현
- 예시에서 opacity.jap를 그대로 사용하지 않고 검은 부분을 밝을 회색으로 바꾸어서 사용한다.
- 해보니 완전 투명해져서 아무것도 없는 것처럼 보인다. 예시에서는 반투명 유리창 느낌. 아마 회색으로 바꾸어서 사용해서 그런 것 같다.
투명도와 관련된 속성으로 transparent 속성도 추가해야 한다.
alphaToCoverage 속성으로 투명효과를 다르게 표현 가능
결과물이 예시와 다르다!!
수평방향으로 텍스쳐 이미지의 반복수 가 다른데 이걸 변경하기 위해서는
useEffect에서 textures.map.repeat.x = textures.displacementMap.repeat.x = textures.aoMap.repeat.x = textures.roughnessMap.repeat.x = textures.metalnessMap.repeat.x = textures.normalMap.repeat.x = textures.alphaMap.repeat.x = 4를 추가하여 반복 수를 4번 반복하도록 바꾼다.
하지만 텍스쳐가 원통을 전부 감싸지 못하는데 이걸 해결하기 위해서
textures.map.repeat.wrapS = textures.displacementMap.wrapS = textures.aoMap.wrapS = textures.roughnessMap.wrapS = textures.metalnessMap.wrapS = textures.normalMap.wrapS = textures.alphaMap.wrapS = THREE.MirroredRepeatWrapping를 추가하여 모든 텍스쳐 객체에 대해서 wrapS값을 THREE.MirroredRepeatWrapping으로 변경하고 있다.
wrapS는 반복이 시작되는 시점에서 어떻게 텍스쳐 이미지를 사용할지 결정하는 코드(wrapT는 수직 방향)
THREE.MirroredRepeatWrapping - 찾아보니까 RepeatWrapping까지만 나오는데 왜 그런것일까?? mirrored를 빼도 되는지 해봐야겠다. - 해보니까 둘다 된다.
textures.map.needsUpdate = textures.displacementMap.needsUpdate = textures.aoMap.needsUpdate = textures.roughnessMap.needsUpdate = textures.metalnessMap.needsUpdate = textures.normalMap.needsUpdate = textures.alphaMap.needsUpdate = true를 통해서 업데이트까지 해야한다.
그럼에도 불구하고 다른 부분이 아직까지 있다.
이유는 광원의 차이, 3d렌더러 엔진의 차이가 있고, 기존 이미지는 Procedural Material로 만들었기 때문이다.
Procedural Material은 사실적인 3d결과물을 만들 수 있으며 R3F같은 실시간 렌더링 엔진에서는 사용불가하다. Procedural Material을 텍스처 이미지로 만드는 것을 배이킹이라고 하고 이걸 개발에 사용해야한다.

댓글남기기